Detecção 5-hmC
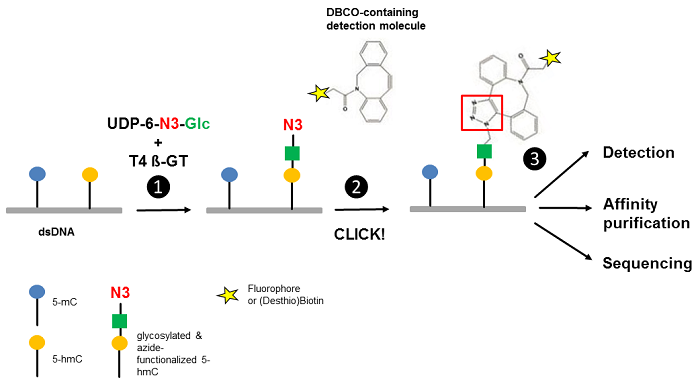
Figure 1 Workflow of 5-hmC detection. Step 1: T4 Phage ß-glycosyltransferase (T4 ß-GT)-mediated glycosylation and simultaneous azide-functionalization of 5-hmC residues using UDP-6-azide-glucose (UDP-6-N3-Glc). Step 2: Copper-free labeling of Azide (N3) with DBCO-containing detection molecule (DBCO-containing (Desthio)Biotin or DBCO-containing Fluorescent Dyes ) forming a stable triazole moiety. Step 3: Detection, affinity purification or sequencing of 5-hmC containing DNA (modified according to [3]).
Produtos
Selected References
[1] Branco et al. (2012) Uncovering the role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the epigenome. Nature Reviews Genetics 13:7.
[2] Huang et al. (2010) The behaviour of 5-hydroxymethycytosine in bisulfite sequencing. PLOS One 5(1):e8888.
[3] Song et al. (2011) Selective chemical labeling reveals the genome-wide distribution of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nature Biotech 29(1):68.
[4] Li et al. (2012) Selective Capture of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine from Genomic DNA. J. Vis. Exp. 68:e4441.
[5] Song et al. (2016) Simultaneous single-molecule epigenetic imaging of DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation. PNAS 113(16):4339.
